프랙탈
on Processing
프랙탈(fractal)은 세부 구조가 끊임없이 전체 구조를 되풀이하는 현상이다. 프랙탈을 스케치하기 위해서는 재귀 함수(recursive function)를 사용해야 한다.
규칙성
동일한 도형이 규칙적으로 반복하는 프랙탈을 그려보도록 하겠다.
정삼각형
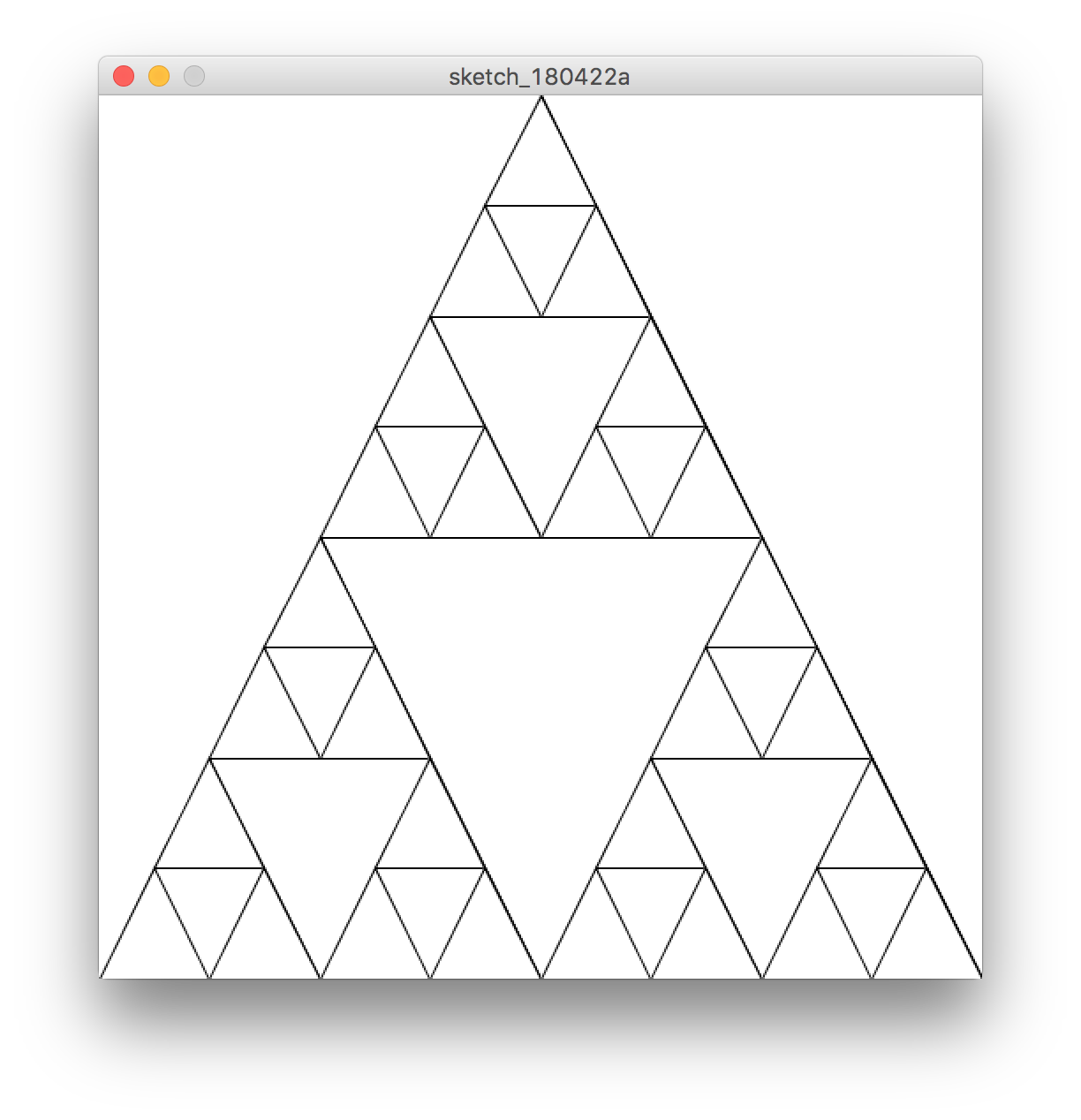
먼저 정삼각형 안에 정삼각형이 존재하는 프랙탈을 그려보자.
void equTri(int x0, int y0, int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int N) {
if(N >= 0) {
triangle(x0, y0, x1, y1, x2, y2);
equTri(x0, y0, (x0 + x1) / 2, (y0 + y1) / 2, (x0 + x2) / 2, (y0 + y2) / 2, N - 1);
equTri((x0 + x1) / 2, (y0 + y1) / 2, x1, y1, x0, y2, N - 1);
equTri((x0 + x2) / 2, (y0 + y2) / 2, x0, y1, x2, y2, N - 1);
}
}
void setup() {
size(500, 500);
background(255);
equTri(width / 2, 0, 0, height, width, height, 3);
}
실행 결과는 다음과 같다.
원
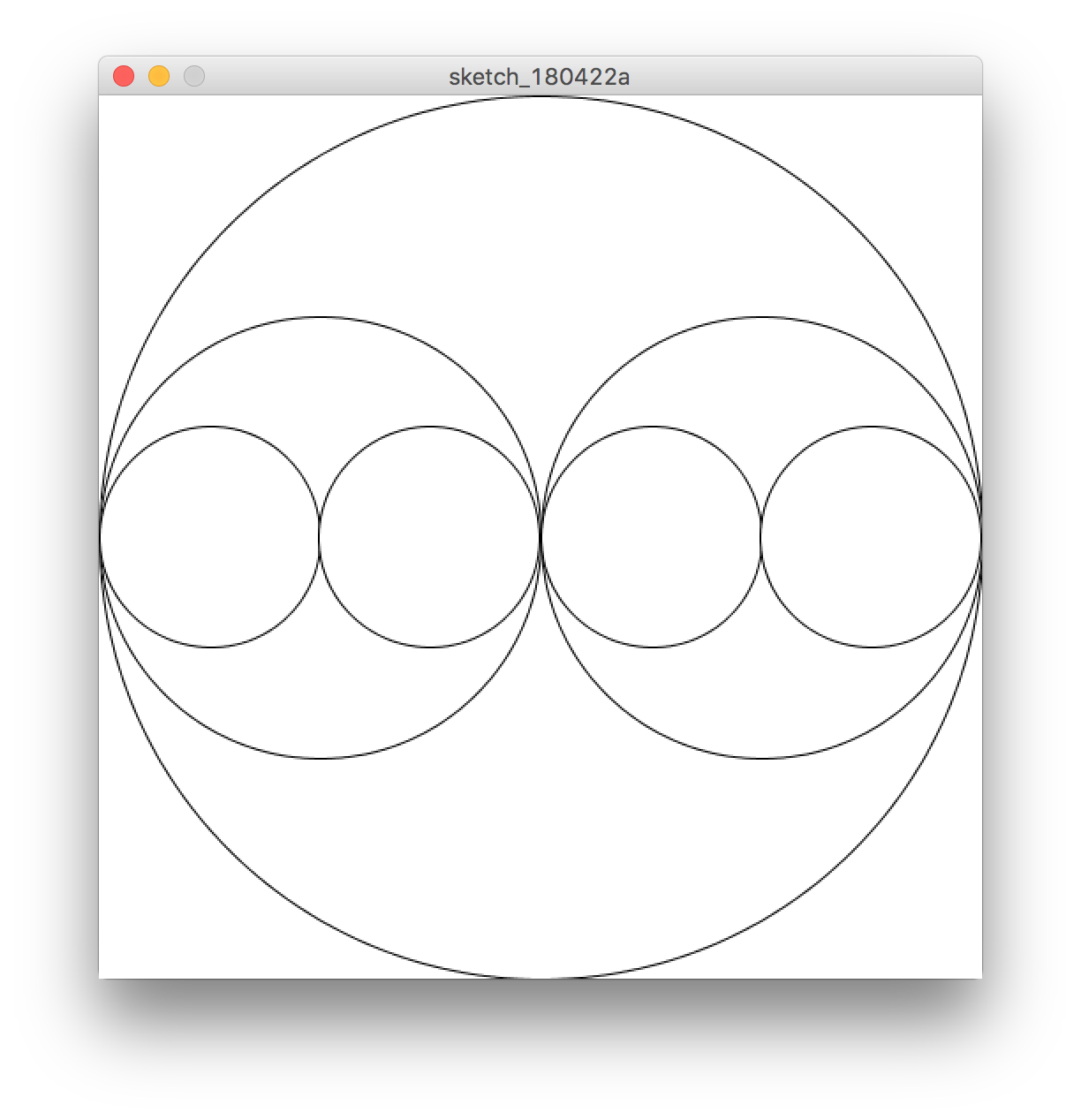
원 안에 원이 반복되는 프랙터를 스케치해보도록 하겠다.
void circle(int x, int y, int diameter) {
if(diameter > width / 8) {
pushMatrix();
translate(x, y);
ellipse(0, 0, diameter, diameter);
circle(- diameter / 4, 0, diameter / 2);
circle(diameter / 4, 0, diameter / 2);
popMatrix();
}
}
void setup() {
background(255);
size(500, 500);
circle(width / 2, height / 2, width);
}
translate(x, y)은 translate(x, y) 호출 이후의 결과를 x축은 x만큼 y축은 y만큼 이동시키는 함수이다. pushMatrix()는 현재 좌표 체계를 스택에 저장하는 함수이고 popMatrix()는 이전 좌표 체계로 되돌리는 함수이다. 즉 pushMatrix()와 popMatrix()는 translate()이 영향을 미칠 수 있는 범위를 설정해준다.
실행 결과는 다음과 같다.
나무
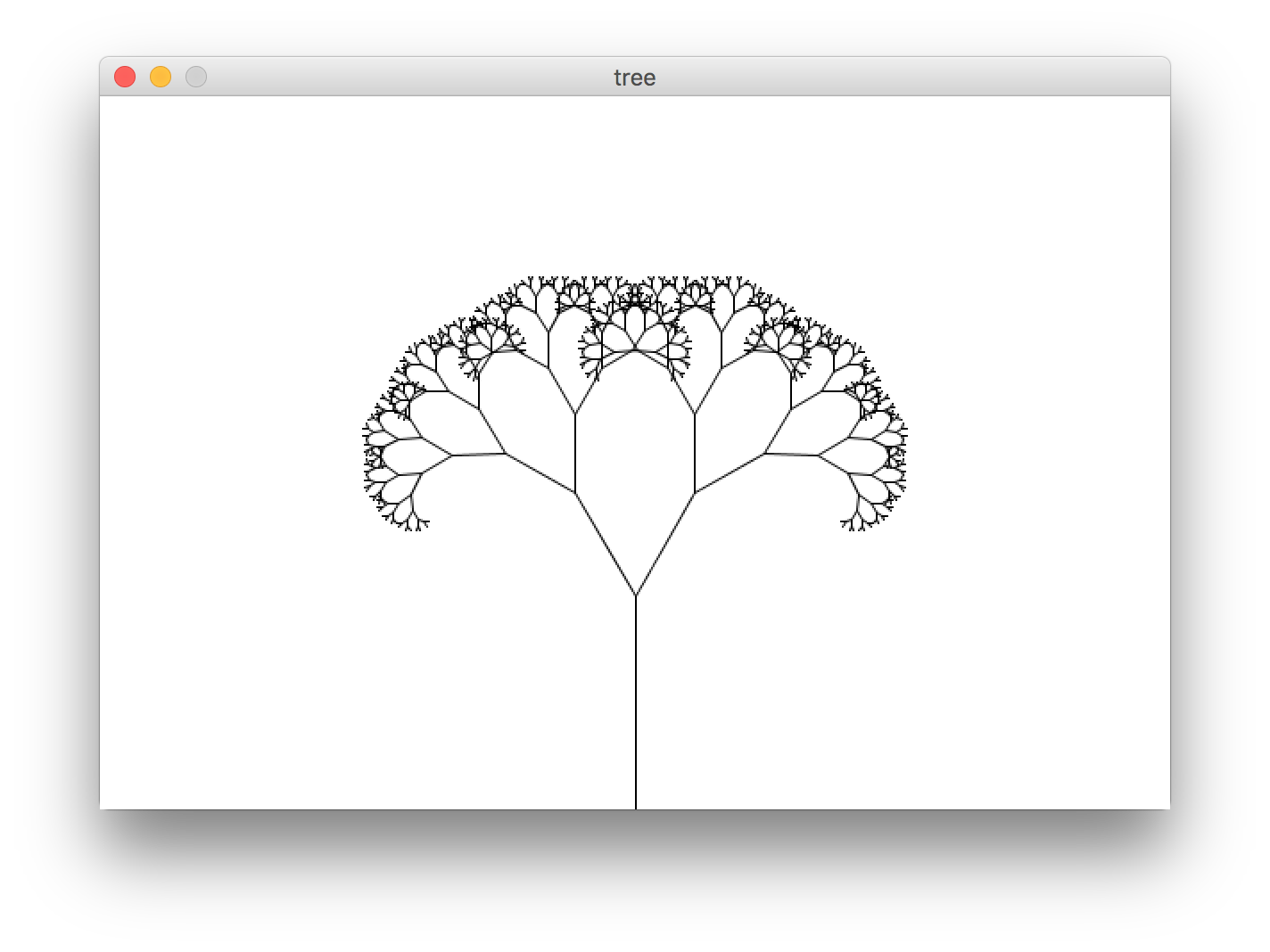
규칙적인 나무를 스케치해보도록 하겠다.
float theta;
void setup() {
size(600, 400);
}
void draw() {
background(255);
stroke(0);
theta = 100;
translate(width/2, height);
line(0, 0, 0, -120);
translate(0, -120);
branch(100);
}
void branch(float h) {
h *= 2.0/3.0;
if(h > 2) {
pushMatrix();
rotate(theta);
line(0, 0, 0, -h);
translate(0, -h);
branch(h);
popMatrix();
pushMatrix();
rotate(-theta);
line(0, 0, 0, -h);
translate(0, -h);
branch(h);
popMatrix();
}
}
결과는 다음과 같다.
불규칙성
랜덤 함수와 조건문을 활용하면 재귀 함수를 활용하여 불규칙적인 프랙탈도 나타낼 수 있다.
몬드리안
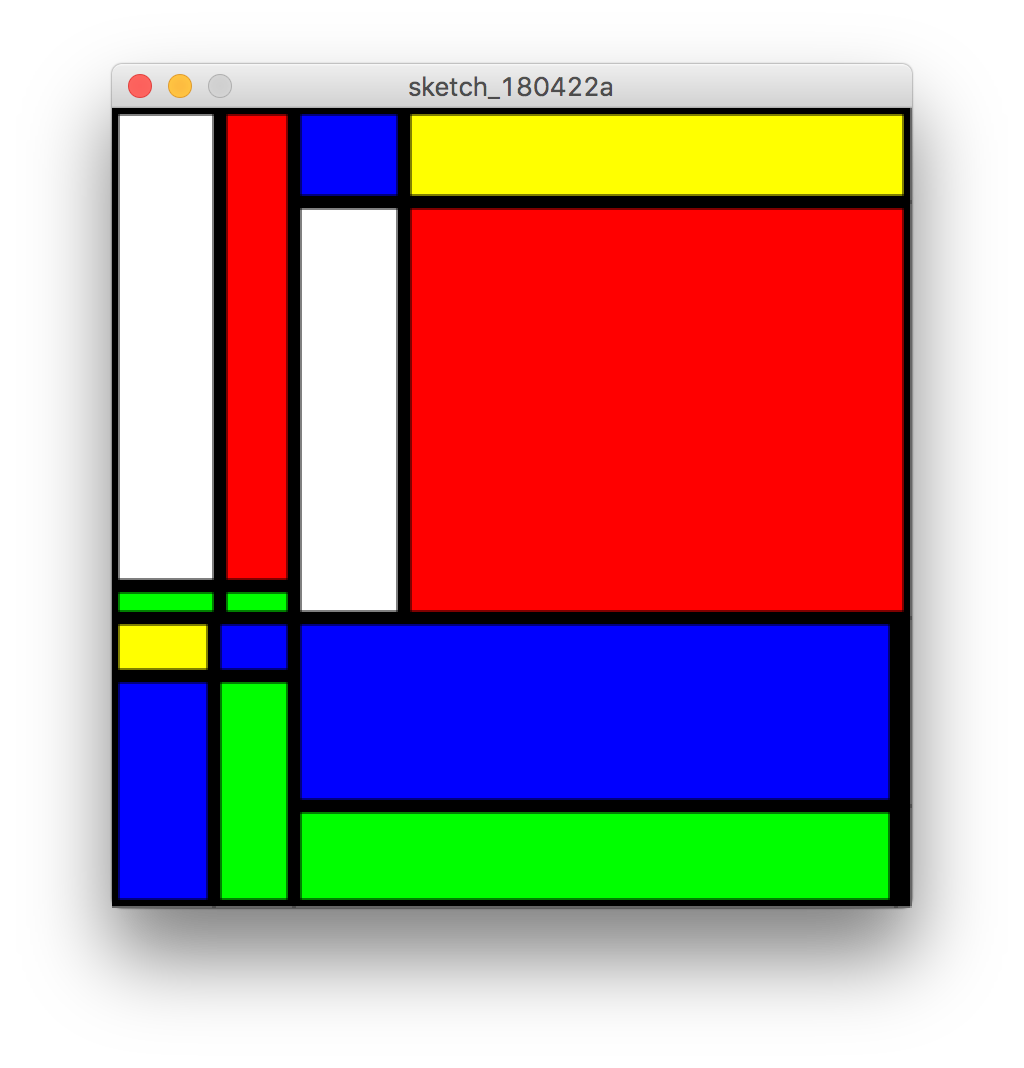
재귀함수를 이용하여 몬드리안 작품과 유사한 결과물을 스케치해보도록 하겠다.
void piet(int x0, int y0, int x1, int y1, int N) {
if(N == 0) {
color c[] = { #ff0000, #00ff00, #0000ff, #ffff00, #ffffff };
fill(c[int(random(c.length))]);
strokeWeight(4);
rect(x0, y0, x1 - x0 - 3, y1 - y0 - 3);
}
else {
int i = int(random(x0, x1));
int j = int(random(y0, y1));
piet(x0, y0, i, j, N - 1);
piet(i, y0, x1, j, N - 1);
piet(x0, j, i, y1, N - 1);
piet(i, j, x1, y1, N - 1);
}
}
void setup() {
size(400, 400);
piet(1, 1, 400, 400, 2);
}
랜덤 함수를 사용하면 몬드리안 유사 작품과 같이 불규칙적인 프랙탈도 그릴 수 있다.
벚꽃 나무
랜덤 함수를 사용하여 규칙적이지 않은 벚꽃 나무를 그려보도록 하겠다.
void setup() {
size(600, 600, P3D);
smooth();
noLoop();
}
void draw() {
background(255);
strokeWeight(10);
for(int i = -300; i <= 300; i += 80) {
pushMatrix();
translate(width/2 + i, height - 20, i);
branch(0);
popMatrix();
}
}
void branch(int depth) {
if(depth < 12) {
line(0, 0, 0, -height/10);
{
translate(0, -height/10);
rotate(random(-0.1, 0.1));
if(random(1.0) < 0.6) {
rotate(0.3);
scale(0.7);
pushMatrix();
branch(depth + 1);
popMatrix();
rotate(-0.6);
pushMatrix();
branch(depth + 1);
popMatrix();
}
else {
branch(depth);
}
}
}
else {
noStroke();
fill(#FFBFF9, 150);
ellipse(0, 0, random(100, 300), random(100, 300));
stroke(0);
}
}
void mouseReleased() {
redraw();
}
결과는 다음과 같다.
